Jul 28th 2022 - Monica Cunanan
What is Refrigerant? Uses, Risks and Laws
Refrigerant is important for keeping things cold and cool, but it's not usually something most people think about when buying a refrigerator or an air conditioner. However, with regulations changing and some refrigerant types becoming illegal (such as R22), it is important to know the differences between different types of refrigerant when deciding which type to use for replacement purposes.
What is Refrigerant?
A Refrigerant is an agent used for cooling that absorbs heat and allows cool air to pass through it when it passes through a compressor and evaporators. As it goes through the thermodynamical process, it changes between a liquid or gas
Refrigerants are substances used in a heat cycle that transfers heat from one area to another. Usually a gas at normal room temperature. Most refrigerants are used for cooling purposes.
Different Types of Refrigerant
For compliance with refrigerant regulations, consider if your refrigerant is environmentally friendly when buying new heavy equipment or appliance. Check out if your commercial refrigerators are environmentally-friendly.
| Types of Refrigerant | Components | Uses | ODP | GWP | Eco-Friendly? | Flammable | Banned? |
| R-12 | ChloroFluoroCarbons (CFC), Methane Based | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 1 | High (10900) | No | No | Banned in 1994 |
| R-22 | HydroChloroFluoroCarbons (HCFC), contains less chlorine than CFCs | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 0.055 | Medium (1810) | No | No | Will be banned by 2030 |
| R-290 (aka Care 40) | HydroCarbons (HC), Propane based | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 0 | Low (6) | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| R-134A | HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC) | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 0 | 1430 (Medium) | Somewhat | No | N/A |
| R-404A | HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC) | Refrigerators and Freezers | 0 | High (3922) | No | No | N/A |
| R-410A | HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC) | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 0 | Medium (2088) | Somewhat | No | N/A |
| R-450A | HydroFluoroCarbon (HFC) | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 0 | Medium (547) | Yes | No | N/A |
| R-513a (aka Opteon XP10) | Azeotropic HFC+HFO blend | Refrigerators and Air Conditioners | 0 | 573 | Yes | No | N/A |
| R-600a (aka Care 10 or Isobutane) | Isobutane | Commercial and residential establishments | 0 | Low (3) | Yes | Yes | N/A |
The Use of Refrigerants and How it Works
- The refrigerant absorbs heat from the inside of the refrigerator or AC and then releases it into the surrounding air.
- As the refrigerant enters the compressor in your air conditioner it turns into a gas.
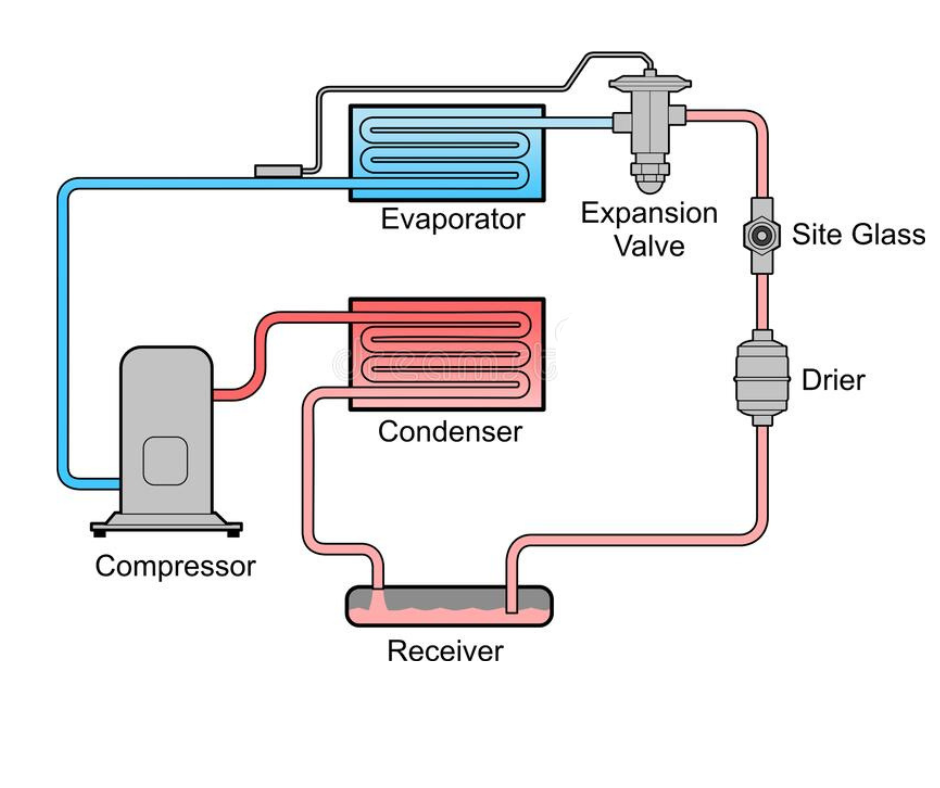
- It expands and cools because of the sudden drop in pressure, turning it into a gas.
- When the gaseous refrigeration fluid passes through the copper evaporator coil inside the unit, the heat absorbed by the fluid causes the liquid to turn into vapor.
- The compressor then draws the refrigerant gas and absorbs the heat out of the food products, increasing its pressure.
- After passing through the condenser coils, the hot, high-pressure gas cools down. As it does so it radiates its heat out into space and then absorbs that heat from space and converts it back into liquid form.
- As the liquid refrigerant enters the expansion device, the process starts again.
The Importance of Refrigerant Regulations
Refrigerant regulations form part of the government’s Climate Action Plan, which aims to reduce emissions from refrigerators and air conditioners. Through a program under the Clean Air Act, SNAP, the EPA continues to assess all chemicals and substances that could deplete the ozone layer Refrigerant Monitoring helps the EPA determine which types of refrigerants are safe and environmentally friendly. Ozone depletion potential (ODP) is calculated by measuring an ozone-depleting chemical’s atmospheric lifetime, the molecular weights of any bromine and chlorine atoms it contains, and its ability to undergo photochemical decomposition. The higher the ozone depletion number, the worse that particular type of refrigerant is for the atmosphere.
Refrigerant is essential for cooling refrigerators and air conditioners but it generally isn't a factor most people think about when making a purchase. However, with refrigerant laws changing and certain refrigerant types becoming illegal, it is important to understand the differences between the types of refrigerant when it comes to replacing your refrigerator or freezer.
How Refrigerants affect Global Warming
Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP)
- Between zero and one.

- The closer the refrigerating agent measures to 1, the worse for the ozone layer.
- Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are chemicals that contain chlorine. They include Freon and CFCs. These chemicals are known to deplete the Earth’s protective ozone layer.
Global Warming Potential (GWP)
- Between 0 and 2500 and above
- A GWP less than 150 would be considered a low GWP, between 150 and 2500 would be a medium GWP, and greater than 2500 is a high GWP.
- Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) have the highest Global Warming Potential
Refrigerants with zero ozone depletion potential (ODP) would be considered environmentally friendly but not green because they still have the potential for contributing to GHH.
Laws About Refrigerant
Refrigerant regulations exist because they negatively affect the environment. They list various refrigerant types that are currently banned and that will be phased out soon. There are plenty of laws in place to protect consumers and our environment.

- Once the most popular refrigerant, R-12 has been banned since the early 1990s due to its contribution to global warming. Production ended in 1994.
- Refrigerant R-22 was developed in the late 1990s to temporarily replace R12 because it has a lower ozone depletion potential (ODP). Production is expected to stop in 2020 and it will become completely illegal to comply with the Clean air act of 2010 by 2030.
- Refrigerant leaks need to be repaired within 30 days and refrigerants must be recovered, recycled, and disposed of correctly by a certified technician to prevent fines.
- Dispose of refrigerators and air conditioners properly by following EPA regulations.
Knowing the laws and regulations regarding refrigeration can be extremely helpful when deciding which type of commercial refrigerator is right for your business.
Significant New Alternatives Policy (SNAP) Program

It dictates that Class I and II refrigerants must be tightly controlled. Refrigerants include commercial kitchen equipment, reach-in freezer units, air conditioning systems, and many other products The EPA has also added two new refrigerants with a lower Global Warming Potential (GWP), and changed some rules regarding refrigerant disposal.
Exceptions:
Eventually, the EPA plans to ban class II refrigerants completely from commercial and residential use by 2030. Until then, the use of these substances has been restricted, but there are some exceptions. For example, you could use Class II refrigerants if they were recycled or used in older fridges.
Need Commercial Refrigeration for your business?
Here at Culinary Depot, we carry different types of commercial refrigeration that are perfect for any business.
May it be:
- Reach-In Refrigerators and Freezers
- Prep Refrigeration
- Merchandising & Display Refrigeration
- Undercounter Refrigerators
- Bar Refrigerator
- Undercounter Freezer
- Worktop Freezers
- Worktop Refrigerators
Contact us or visit our online store for more information about any commercial machines to keep your produce fresh!